2019.04.05
Medical news
Visit to a U.S. Farm
On March 25 and 26, 2019, we attended a meeting and visited a farm in Wisconsin, USA to discuss products developed in-house.
Japanese and U.S. experts were invited to the meeting, and there was an active exchange of opinions on the actual condition of dairy farming and issues.
Through the farm visit, we learned about the commonalities and differences between Japan and the United States, such as the size of farms in the country and livestock management methods.

Number of dairy cattle: 2,250, medium-sized farm
It is common to press out milk 3 times a day per cattle.

The health control of dairy cattle is implemented by a person in charge on a daily basis.

Each cow is marked with the date of delivery.

A stethoscope is used to check for abomasal displacement, which may give rise to the loss of appetite.
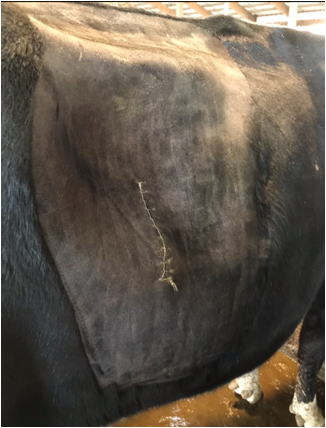
If abomasal displacement is diagnosed, surgery is performed to put the stomach back in place.

Monitoring of the rumination of cows, etc. is possible since a heart rate measurement device and microphone are built in.

Infusions and injections are also used for treatment.


[Milking parlor] The blue unit automatically measures BHBA, etc. at milking. 1 unit: $2,000


For cows with ketosis that have lost appetite, supplements are injected directly with a pump by inserting a tube into the stomach.

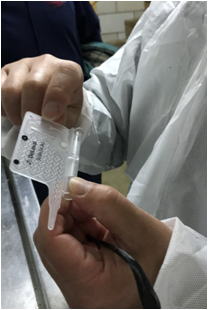
Laboratory in the farm
Medium-sized or larger farms in the United States have facilities like this.

Meeting

Equipment demonstration



